
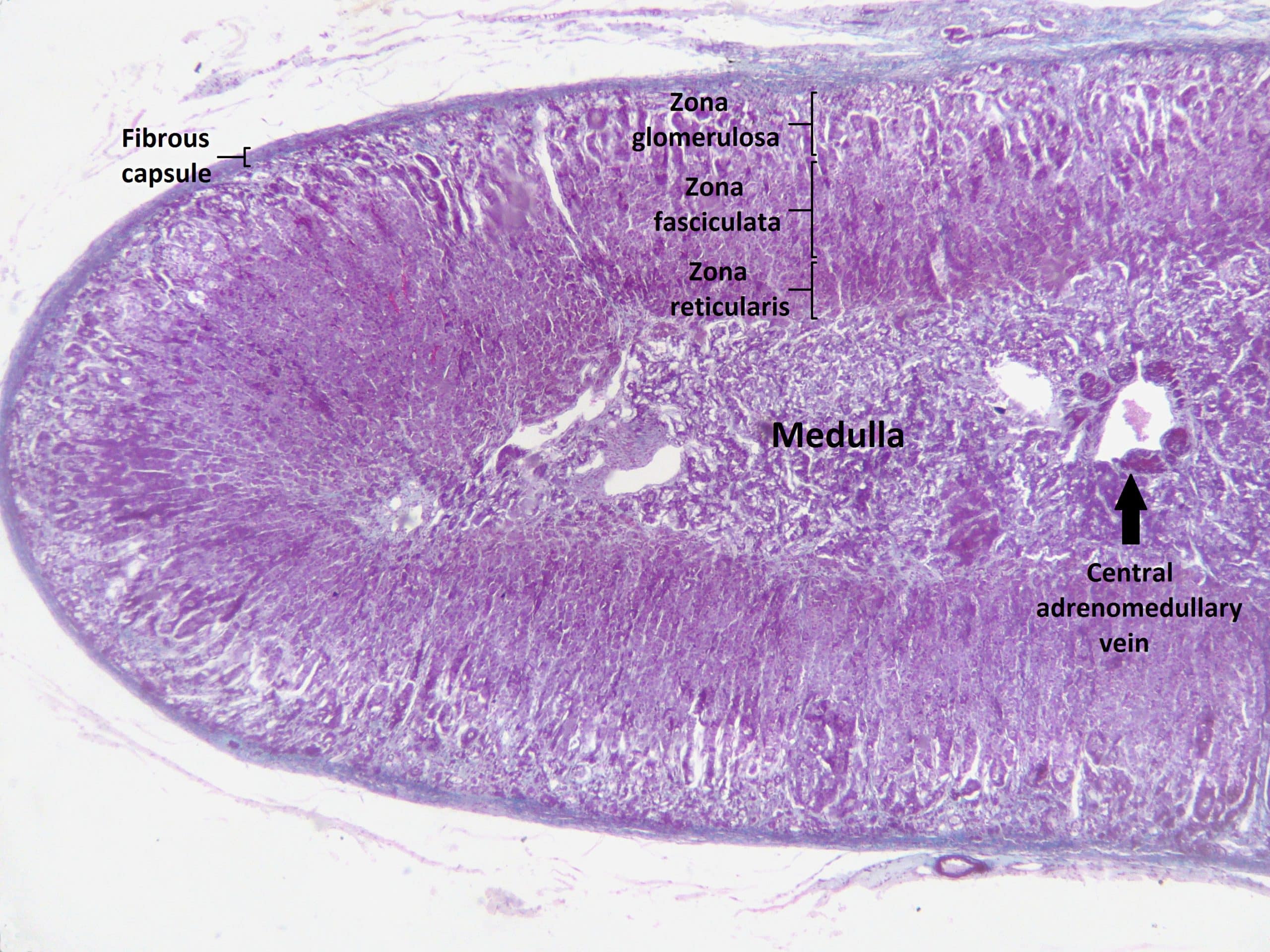
The fetal cortex develops in the centre, with the permanent cortex surrounding it. The adrenal cortex develops from the intermediate mesoderm. Mesodermal cells then surround the medulla. The medulla originates from neural crest cells migrating from sympathetic ganglion. The adrenal glands develop from two separate embryological tissues the neural crest ectoderm and the intermediate mesoderm. The adrenal medulla represents only 10-20% of the adrenal gland. Through sympathetic preganglionic fiber stimulation, the medullary cells secrete catecholamines. The medulla acts as a sympathetic ganglion with the postganglionic cells lacking axons. In fetal life, the adrenal medulla plays a role in the autonomic nervous system. The adrenal medulla is primarily involved in the production of catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine.
The adrenal cortex represents 80-90% of the adrenal gland. From the outer to inner, the layers are Īll these zones produce hormones derived from cholesterol, which is abundant in the cells. The adrenal cortex is red to light brown in colour and is composed of three zones. The glands consist of two layers the cortex and medulla. The adrenal glands are paired bodies lying cranial to the kidneys within the retroperitoneal space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
